Addiction
The impact of relaxation of methadone take-home protocols on treatment outcomes in the COVID-19 era

Increased distance was associated with lower daily attendance to an opioid treatment program in Spokane County Washington
Adherence to opioid agonist therapy using methadone is associated with improved clinical and community outcomes such as reductions in drug use, criminal behavior, high-risk sexual behavior, and mortality. Unfortunately, however, the need to have patients’ methadone ingestion witnessed at the clinic on a daily basis may comprise adherence. In this study we found significant positive associations between distance to an Opioid Treatment Program (OTP) and the number of missed doses in the first month of treatment. Findings suggest the need to improve the spatial availability of OTPs to optimize opioid use disorder treatment outcomes.

Spatial access to opioid treatment program and alcohol and cannabis outlets: analysis of missed doses of methadone during the first, second, and third 90 days of treatment
Background: The burden of access to opioid treatment programs (OTPs) may change as clients become eligible for take-home privileges. Our previous study showed clients who lived more than 10-miles away from an OTP were more likely to miss methadone doses during the first 30 days of treatment. Proximity to alcohol and cannabis outlets may also negatively influence treatment adherence.
Objective: To examine the association between access to this OTP, alcohol and cannabis outlets, and the number of missed methadone doses during the first, second, and third 90 days of treatment.
Methods: The number of missed methadone doses was calculated for 752, 689, and 584 clients who remained in treatment, respectively, for at least 3, 6, and 9 months (50% female). Distance between client’s home and the OTP, alcohol, and cannabis outlets was measured. Generalized linear models were employed.
Results: Shorter distance from a client’s residence to the OTP was associated with a decreased number of missed methadone doses during the first 90 days of treatment. Shorter distance to the closest cannabis retail outlet was associated with an increased number of missed methadone doses during the first and second 90 days of treatment. Shorter distance to the closest off-premise alcohol outlet was associated with an increased number of missed methadone doses during the third 90 days of treatment.
Conclusions: Improving spatial accessibility of OTPs are essential to ensure treatment opportunities are available for individuals so affected. Exploring to what extent residing in areas that facilitate alcohol and cannabis availability can influence treatment adherence is warranted.

Three-year retention in methadone opioid agonist treatment: A survival analysis of clients by dose, area deprivation, and availability of alcohol and cannabis outlets
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of clinical, socio-demographic, and contextual characteristics on treatment retention in an opioid treatment program (OTP).Using a retrospective longitudinal review of 851 clients who received methadone at the only state-funded OTP in Spokane County, Washington between 2015 and 2017. A time variable (the number of days in treatment) and a status indicator (to distinguish between clients who dropped out or censored) worked together to define retention in treatment. Our hypothesized covariates included: area deprivation, distance to the OTP, availability of cannabis retail outlets, availability of on-premise and off-premise alcohol outlets, methadone dosage, age, gender, race, and years on treatment. Cox regression within the family of survival analysis was used to model time-to-event data in the presence of censored cases.
That results showed that the median duration of retention was 394 (95%CI = 324–464) days. In the multivariable Cox regression, factors predicting treatment retention were area deprivation (HR = 1.79, 95%CI = 1.02–3.15, p = 0.04), age (HR=0.99, 95%CI=0.98-.99, p = 0.008), dosage of methadone (HR=0.98, 95%CI=0.98-0.98, p < 0.001), and the number of years on treatment (HR=1.12, 95%CI=1.06-1.18, p < 0.001).
The findings of this study showed age and methadone dosage were protective factors and area deprivation and years on treatment were risk factors for treatment retention. After dichotomizing methadone dosage, a unique finding of this study was that higher dosage of methadone did not lead to increasingly smaller HRs for dropping out of treatment. Considering that opioid use disorder is a chronic condition, efforts need to be made to target factors associated with retention.

Distance to HIV care and treatment adherence: Adjusting for socio-demographic and geographical heterogeneity
Distance to health services plays an important role in determining access to care and an individual's health. This study aims to examine the relationship between distance to antiretroviral therapy (ART) prescribing physician and adherence to HIV treatment in British Columbia, Canada. Only participants who provided highly accurate locational data for both place of residence and their physician were used in the analysis. Using logistic regression, a multivariable confounder model was created to assess the association between distance and adherence. A geographically weighted logistic regression was also performed to adjust for spatial dependency. There were 1528 participants in the analysis, for a median distance of 17.85km. The final model showed further away from ART prescribing physician had a higher chance of incomplete adherence to ART (adjusted odds ratio 1.31; 95% Confidence Interval 1.04–1.65). Mobile services could potentially increase adherence rates for population residing further away from their ART prescribing physician.

Media Exposure and Substance Use Increase during COVID-19
Background
Lockdown measures because of COVID-19 are likely to result in deteriorating physical and mental health. In this study, our aim was to assess the impact of media exposure on increases in substance use during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
A nationally representative online survey of 1264 adults was collected during the pandemic in the United States. Logistic regression was used to explore the association between an increase in substance use since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic and exposure to cable news or social media together with COVID-19 knowledge, while controlling for covariates.
Results
Study participants with the highest exposure to social media (at least daily) and low knowledge of COVID-19 were 9.9 times more likely to experience an increase in substance use since the pandemic began. Participants with the highest exposure to cable news and low knowledge of COVID-19 were over 11 times more likely to experience an increase in substance use.
Discussion
Based on our findings, we recommend that media organizations should aim to reduce uncertainty and also provide positive coverage to counter the negative information associated with pandemics.
Conclusions: Improving spatial accessibility of OTPs are essential to ensure treatment opportunities are available for individuals so affected. Exploring to what extent residing in areas that facilitate alcohol and cannabis availability can influence treatment adherence is warranted.

Enviromental Health
Environmental Correlates of Reaching a Centenarian Age: Analysis of 144,665 Deaths in Washington State for 2011−2015
This study examined the association of several social and environmental factors on the likelihood of reaching centenarian age for older adults in Washington State.
increased neighborhood walkability, lower education level, higher socioeconomic status, and a higher percent of working age population were positively associated with reaching centenarian age.Being widowed, divorced/separated, or never married were also positively correlated compared to being married. Additionally, being white or female were positively correlated with reaching centenarian status.
Several social and environmental factors are correlated with becoming a centenarian in Washington State. In this study, we explore findings that are consistent with previous research, as well as some that have not been previously explained. More research is needed to expand upon these findings in this rapidly growing field
Estimated Residential Exposure to Agricultural Chemicals and Premature Mortality by Parkinson’s Disease in Washington State
The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between estimated residential exposure to agricultural chemical application and premature mortality from Parkinson’s disease (PD) in Washington State. Washington State mortality records for 2011–2015 were geocoded using residential addresses, and classified as having exposure to agricultural land-use within 1000 meters. Generalized linear models were used to explore the association between land-use associated with agricultural chemical application and premature mortality from PD. Individuals exposed to land-use associated with glyphosate had 33% higher odds of premature mortality than those that were not exposed (Odds Ratio (OR) = 1.33, 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) = 1.06–1.67). Exposure to cropland associated with all pesticide application (OR = 1.19, 95% CI = 0.98–1.44) or Paraquat application (OR = 1.22, 95% CI = 0.99–1.51) was not significantly associated with premature mortality from PD, but the effect size was in the hypothesized direction. No significant associations were observed between exposure to Atrazine (OR = 1.21, 95% CI = 0.84–1.74) or Diazinon (OR = 1.07, 95% CI = 0.85–1.34), and premature mortality from PD. The relationship between pesticide exposure and premature mortality aligns with previous biological, toxicological, and epidemiological findings. Glyphosate, the world’s most heavily applied herbicide, and an active ingredient in Roundup® and Paraquat, a toxic herbicide, has shown to be associated with the odds of premature mortality from PD.

GPS-based built environment measures associated with adult physical activity
Studies often rely on home locations to access built environment (BE) influences on physical activity (PA). We use GPS and accelerometer data collected for 288 individuals over a two-week period to examine eight GPS-derived BE characteristics and moderate-to-vigorous PA (MVPA) and light-to-moderate-vigorous PA (LMVPA). NDVI, parks, blue space, pedestrian-orientated intersections, and population density were associated with increased odds of LMVPA and MVPA, while traffic air pollution and noise were associated with decreased odds of LMVPA and MVPA. Associations varied by population density and when accounting for multiple BE measures. These findings provide further information on where individuals choose to be physically active.
Health Equity
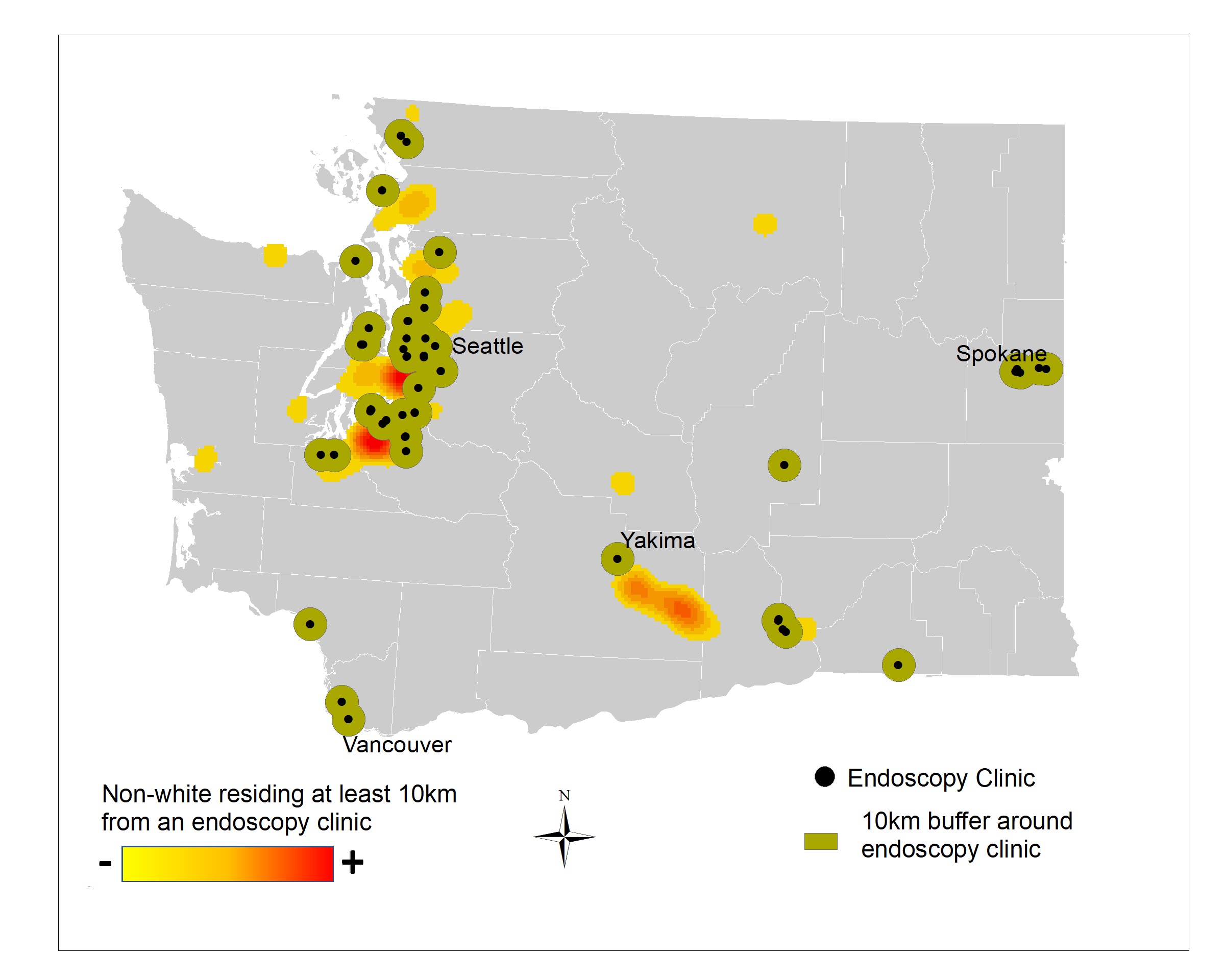
Distance to endoscopy services amplifies racial inequities in colorectal cancer mortality in Washington state
Background: This study evaluates relationships among race, access to endoscopy services, and colorectal cancer (CRC) mortality in Washington state (WA).
Methods: We overlayed the locations of ambulatory endoscopy services with place of residence at time of death, using Department of Health data (2011-2018). We compared CRC mortality data within and outside a 10km buffer from services. We used linear regression to assess the impact of distance and race on age at death while adjusting for gender and education level.
Results: Race impacted age at death: 72.9y vs. 68.2y for white vs. non-white (p below 0.001). The adjusted model showed that non-whites residing outside the buffer died 6.9y younger on average (p below 0.001). Non-whites residing inside the buffer died 5.2y younger on average (pbelow 0.001), and whites residing outside the buffer died 1.6y younger (p below 0.001). We used heatmaps to geolocate death density.
Conclusion: Results suggest that geographic access to endoscopy services disproportionately impacts non-whites in Washington. These data help identify communities which may benefit from improved access to alternative colorectal cancer screening methods.
Socioeconomic and Racial Inequities in Breast Cancer Screening During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Washington State
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted preventive care, including cancer screening.
In this study, we used clinical data to examine differences in breast cancer screenings before and during the COVID-19 pandemic overall and among sociodemographic population groups.
Data included completed screening mammograms within a large statewide nonprofit community health care system in Washington State between April 1, 2018, and December 31, 2020.
Among the 55 678 screenings in April to December 2019, 45 572 patients were non-Hispanic White (81.8%), 54 620 patients lived in urban areas (98.1%), and 22 761 patients were commercially insured (40.9%); the mean (SD) age was 62.0 (11.3) years.
We observed greater and significant reductions in the number of screenings from 2019 to 2020 for women who were Hispanic (1727 vs 619; −64.2%), American Indian/Alaska Native (215 vs 84; −60.9%), mixed race (1892 vs 828; −56.2%), Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander (365 vs 166; −54.5%), Asian (2779 vs 1265; −54.5%), and Black (2320 vs 1069; −53.9%) compared with women who were White (45 572 vs 23 163; −49.2%). Women living in rural areas experienced greater reduction in screenings compared with their urban counterparts. In terms of insurance, women who self-paid for treatment and who were insured by Medicaid experienced the largest reduction in screening, whereas those with commercial insurance or Medicare showed smaller reductions.
This study found a substantial overall decline in breast cancer screening in women living in Washington State during the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as inequities in this decline.
Area deprivation amplifies racial inequities in premature mortality in WA state
In the United States, place of residence and racial identity are closely tied to health and wellbeing. A large body of evidence has confirmed that whites living in more-affluent areas have the best chances of a long, healthy life. However, less is known about if and how race and neighborhood deprivation interact in relation to health. In this epidemiological study, we analyzed 242,667 deaths in WA state, for which we could obtain information about the last residential address for each individual at the time of their death. Addresses were used to determine decedents’ exposure to deprivation based on the Area Deprivation Index. We also classified decedents’ race using federal racial categories, as well as their education, gender, and other socioeconomic and demographic characteristics. Our resutls show that deaths among non-whites from deprived neighborhoods were between three and eight times more likely to be premature compared to more-affluent whites.

Eastern Washington Health Profile
The Eastern Washington Health Report aims evaluated the community health status and health issues known to affect individuals and communities in eastern Washington. We compared this region of the state and its distinctly different set of health and social issues to those in western Washington.

The Association Between Obesity, Socio-Economic Status, and Neighborhood Environment: A Multi-Level Analysis of Spokane Public Schools
Socio economic inequities in obesity have been attributed to individuals’ psychosocial and behavioral characteristics. School environment, where children spend a large part of their day, may play an important role in shaping their health. This study aims to assess whether prevalence of overweight and obesity among elementary school students was associated with the school’s social and built environments. Analyses were based on 28 public elementary schools serving a total of 10,327 children in the city of Spokane, Washington. Schools were classified by percentage of students eligible for free and reduced meals (FRM). Crime rates, density of arterial roads, healthy food access, and walkability were computed in a one-mile walking catchment around schools to characterize their surrounding neighborhood. In the unadjusted multilevel logistic regression analyses, age, sex, percentage of students eligible for FRM, crime, walkability, and arterial road exposure were individually associated with the odds of being overweight or obese. In the adjusted model, the odds of being overweight or obese were higher with age, being male, and percentage of students eligible for FRM. The results call for policies and programs to improve the school environment, students’ health, and safety conditions near schools.

Bring Your Own Location Data: Use of Google Smartphone Location History Data for Environmental Health Research
Example of GTL data coverage for one individual
Temporal coverage of GTL data provided by 61 individuals. Each colored box represents the percentage of individuals who had data for the given day. In 2019 and 2020, almost 60% of the individuals had data for everyday of the year.
Differences in GTL coverage, measured using median number of days and places per day of data, by key individual, geographic and smart phone device characteristics
Deep Learning of Street View Imagery to assess the built enviroment
Segmentation of GSV image (left) and segmented features with trees in green (right). For major built env. features the prediction accuracy is >95%
COVID-19 Research
COVID-19 and inequities in colorectal and cervical cancer screening and diagnosis in Washington State

Introduction Studies have shown that cancer screenings dropped dramatically following the onset of the coronavirus diseases 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. In this study, we examined differences in rates of cervical and colorectal cancer (CRC) screening and diagnosis indicators before and during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Methodology We used retrospective data from a large healthcare system in Washington State. Targeted screening data included completed cancer screenings for both CRC (colonoscopy) and cervical cancer (Papanicolaou test (Pap test)). We analyzed and compared the rate of uptake of colorectal (colonoscopies) and cervical cancer (Pap) screenings done pre-COVID-19 (April 1, 2019–March 31, 2020) and during the pandemic (April 1, 2020–March 31, 2021). Results A total of 26,081 (12.7%) patients underwent colonoscopies in the pre-COVID-19 period, compared to only 15,708 (7.4%) patients during the pandemic, showing a 39.8% decrease. A total of 238 patients were referred to medical oncology for CRC compared to only 155 patients during the first year of the pandemic, a reduction of 34%. In the pre-COVID-19 period, 22,395 (10.7%) women were administered PAP tests compared to 20,455 (9.6%) women during the pandemic, for a 7.4% reduction. period 1780 women were referred to colposcopy, compared to only 1680 patients during the pandemic, for a 4.3% reduction. Conclusion Interruption in screening and subsequent delay in diagnosis during the pandemic will likely lead to later-stage diagnoses for both CRC and cervical cancer, which is known to result in decreased survival. Impact The results emphasize the need to prioritize cancer screening, particularly for those at higher risk.
CURE- COVID19 Rural Urban Explorer
The COVID Urban Rural Explorer (CURE) aim to highlight rural urban inequities in COVID trends by county across the US. It also enables users to identify rural counties with both limited hospital capacity and where cases are rapidly growing.
Data-Driven Development of a Small-Area COVID-19 Vulnerability Index for the United States
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to surge in the United States, it has become clear that infection risk is higher in certain populations, particularly socially and economically marginalized groups. Social risk factors, together with other demographic and community characteristics, may reveal local variations and inequities in COVID risk that could be useful for targeting testing and interventions. Yet to date, rates of infection and estimations of COVID risk are typically reported at the county and state level. In this study we develop a small area vulnerability index based on publicly-available sociodemographic data and 668,428 COVID diagnoses reported in 4,803 ZIP codes in the United States (15% of all ZIP codes). The outcome was COVID-19 diagnosis rates per 100,000 people by ZIP code. Explanatory variables included sociodemographic characteristics obtained from the 2018 American Community Survey 5-year estimates. Bayesian multivariable techniques were used to capture complexities of spatial data and spatial autocorrelation and identify individual risk factors and derive their respective weights in the index. COVID-19 diagnosis rates varied from zero to 29,508 per 100,000 people. The final vulnerability index showed that higher population density, higher percentage of noninsured, nonwhite race and Hispanic ethnicity were positively associated with COVID-19 diagnosis rates. Our findings indicate disproportionate risk of COVID-19 infection among some populations and validate and expand understanding of these inequities, integrating several risk factors into a summary index reflecting composite vulnerability to infection. This index can provide local public health and other agencies with evidence-based metrics of COVID risk at a geographical scale that has not been previously available to most US communities.
Development of a vulnerability index for diagnosis with the novel coronavirus, COVID-19, in Washington State, USA
Published and peer reviewed in Health & Place, our COVID-19 vulnerability index utilize demographic, socioeconomic, and medical risk factors can be used to understand population- and community-level variation in susceptibility to COVID-19 across Washington State. Calculate at teh ZIP-code level this index was validated using actual COVID-19 cases from 116 ZIP codes(total of 8,773 COVID-19 diagnoses) from both King and Spokane County in Washignton State.
Hospital Capacity Modeling
The hospital capacity model aims to assist hospitals to predict the future need of essential health care resources as result of Covid19. This web-based model can be used by hospitals and public health organizations to estimate the surge of incoming patients will impact the availability of essential resources such as N95 masks, gowns, gloves, hospital beds, and ventilators. This model relies on user input and will therefore provide an easy and flexible modeling platform requiring minimal technical knowledge.
The need for GIScience in mapping COVID-19
The use of mapping has grown exponentially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Published in Health & Place, this commentary focuses on the use of mapping and Geospatial technique in the era of COVID-19.
COVID-19 hotspots overtime
This animated map showing the growth of COVID-19 cases and deaths across the US since the begining of the pandemic


